Do Foundation Piers Work?

What Are Foundation Piers?
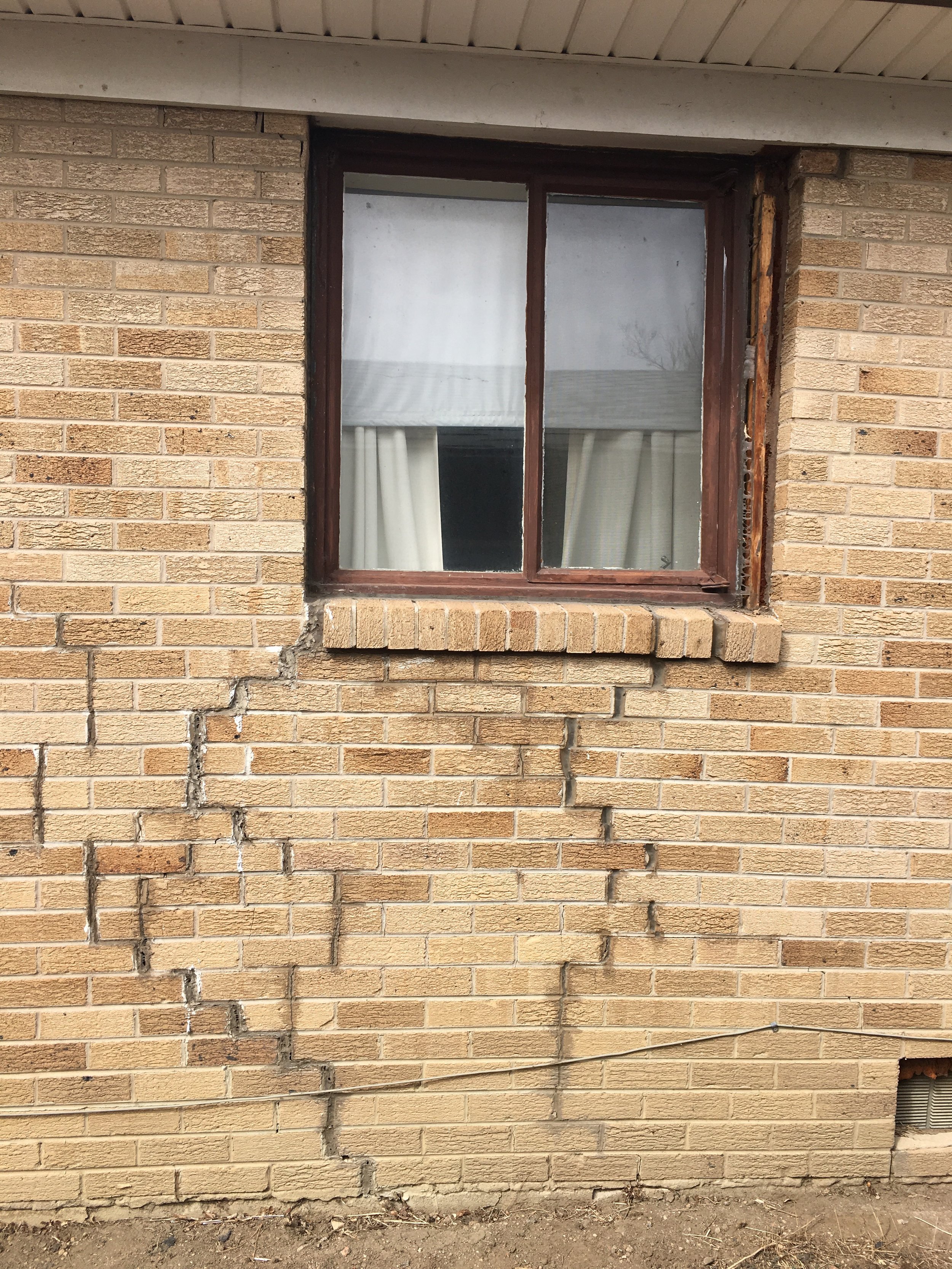
Foundation piers are structural elements designed to support and stabilize foundations that have settled or shifted due to various factors such as soil movement, water infiltration, or construction deficiencies. These piers are installed beneath the foundation footings and extend deep into the ground to transfer the structural load of a building to more stable soil or bedrock layers. Foundation piers play a critical role in preventing further settlement and maintaining the structural integrity of buildings, both residential and commercial.
Types Of Foundation Piers
There are several types of foundation piers commonly used in construction and foundation repair projects. Each type of foundation pier has its unique characteristics and applications, offering different advantages and limitations depending on factors such as soil conditions, structural requirements, and budget constraints.
Concrete Piers reinforced with steel, are durable and ideal for stabilizing foundations by reaching deep into stable soil layers. They're installed by excavating holes beneath the foundation footings and pouring reinforced concrete, offering long-term stability.
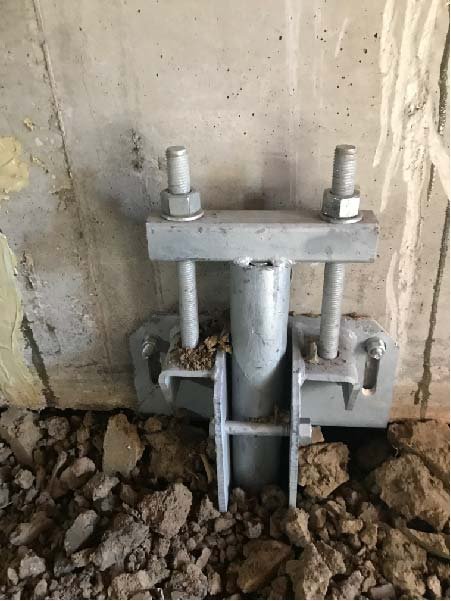
Steel Piers are hydraulically driven into the ground, providing robust support and adjustability to lift and level the foundation precisely. They're resistant to corrosion and suitable for projects requiring accurate elevation control.
Helical Piers featuring helical plates welded to steel shafts, helical piers are efficient in stabilizing foundations on unstable soil. They're versatile, offering immediate lateral support, and can be installed in various soil conditions and terrains with minimal disruption.
Push Piers also called resistance piers, push piers transfer the structural load to stable soil layers by hydraulically driving high-strength steel sections into the ground. They provide stability by leveraging the resistance generated by the surrounding soil, offering flexibility in installation methods and comprehensive stabilization.
How Are Foundation Piers Installed?
The installation of foundation piers typically begins with a thorough assessment of the site by engineers and foundation specialists to determine the appropriate piering method and placement locations. The installation process involves excavating around the foundation to expose the footing, drilling holes for the piers, and inserting the piers to the required depth. Once the piers are in position, hydraulic equipment is used to drive or screw them into the ground until they reach stable soil or bedrock. Load tests may be conducted to ensure the piers can support the structural load of the building effectively. Professional engineers and contractors oversee the entire installation process to ensure compliance with industry standards and local building codes.
How Do Foundation Piers Lift A House?
Foundation piers lift a house or building by providing structural support and transferring the weight of the structure to load-bearing strata beneath the foundation. As the piers are installed and driven into the ground, they exert upward pressure on the foundation, gradually raising it back to its original level. This process effectively stabilizes the foundation and prevents further settlement, restoring the structural integrity of the building. Foundation specialists use precise measurements and advanced equipment to control the lifting process and ensure uniform elevation across the foundation.

Concrete piers lift a house by transferring the structural load to deeper, more stable soil layers. As the concrete cures and hardens, it provides a sturdy foundation, effectively raising the house.
Steel piers lift a house by utilizing hydraulic pressure to drive them deep into the ground. Once in place, the piers are adjusted to lift and level the foundation, providing support and stability throughout the lifting process.
Helical piers lift a house by rotating into the ground like screws, creating a secure anchor in the soil. As the helical piers are installed, they lift the foundation upward, providing immediate support and stabilization.
Push piers lift a house by utilizing hydraulic force to push them into the ground until they reach stable soil layers. As the piers are driven deeper, they gradually lift the foundation, providing continuous support and elevation adjustment.
Typical Cost Of Foundation Piers
The cost of foundation pier installation varies depending on several factors, including the type of pier, the extent of foundation damage, and local labor and material prices. On average, homeowners can expect to pay anywhere from $1,000 to $3,000 per pier for concrete or steel pier installation, with helical piers typically costing slightly more. Additional expenses such as site preparation, engineering fees, and permit costs may also contribute to the overall project cost. It's essential to obtain multiple quotes from reputable foundation repair companies and consult with a professional engineer to determine the most cost-effective solution for your specific needs and budget.
So Do Foundation Piers Really Work?
Foundation piers are a proven and effective solution for stabilizing and repairing foundations affected by settlement or movement. The installation process involves careful assessment, precise placement, and professional oversight to ensure the piers effectively support the structure and prevent further damage. By transferring the structural load to stable soil or bedrock, foundation piers lift and stabilize the foundation, restoring its integrity and preventing future settlement issues. Whether it's concrete piers, steel piers, helical piers, or push piers, each type offers distinct advantages and can be tailored to suit specific project requirements. Despite the initial investment, foundation piers provide a long-lasting solution that can save homeowners from costly structural repairs down the line. With proper installation and maintenance, foundation piers offer peace of mind and ensure the stability and durability of your home or building for years to come.
Foundation problems vary in severity, with some being minor and others posing serious risks. Homeowners can often live in a house with small foundation issues, but waiting too long to address major structural damage can lead to costly repairs, water intrusion, and safety hazards.
Helical piers are an effective solution for lifting and stabilizing homes that have settled due to soil movement or foundation issues. By anchoring deep into stable soil, they restore structural integrity, level floors, and prevent further damage.
Replacing a foundation under an older home is possible but requires expert planning, structural support, and careful execution. While the process can be complex and costly, it provides long-term stability, protects against structural damage, and can even add usable space.
Polyurethane foam may seem like a quick fix for foundation repair, but it fails within a few years, leading to costly removal and repeat repairs. Its environmental impact, lack of long-term stability, and high removal costs make it a poor choice compared to more durable solutions like helical piers or push piers.
A weak foundation can lead to structural damage, uneven floors, water intrusion, and decreased property value if left unaddressed. Recognizing early warning signs and seeking professional foundation repair solutions can help maintain long-term stability and protect your home.
When considering foundation repair in Colorado, timing is crucial for optimal outcomes and cost-effectiveness. Different seasons present unique challenges and advantages for foundation work, so understanding the best time of year for these repairs is essential.
Dealing with a crumbling foundation can be daunting, but with the right approach and professional assistance, it's often possible to address the issues and restore the structural integrity of the foundation.
Understanding the signs of foundation damage is crucial for homeowners to maintain the structural integrity of their properties. Foundation issues can manifest in various ways, from visible cracks in walls to uneven floors and doors that stick.
Foundation repair is a critical process for maintaining the structural integrity of your home. When faced with foundation issues, one of the most common questions homeowners have is, "How long will it take to repair?"
Owning an older home comes with its own set of joys and challenges, particularly when it comes to foundation issues. While every property requires upkeep, older houses often demand extra care due to their age.
Foundation piers play a critical role in preventing further settlement and maintaining the structural integrity of buildings, both residential and commercial. With proper installation foundation piers offer peace of mind and ensure the stability and durability of your home.
Foundation stabilization is essential for maintaining building integrity. Our guide provides an overview of various techniques, helping property owners make informed decisions to address their foundation repair needs effectively.
Understanding the type of foundation your house has is crucial in determining the feasibility of repair. Knowing when it's time to walk away and consider alternative options can save you time, money, and stress in the long run.
Foundation problems can escalate if left untreated, leading to significant structural damage and costly repairs. Understanding the potential consequences of ignoring foundation issues is essential for homeowners and property owners.
Are you noticing signs of potential foundation issues in your home or property? Understanding the common symptoms of foundation damage and the remedies available can help you assess whether foundation repair may be necessary.
Explore the 11 best foundation repair methods available today. Whether you're dealing with cracks, settling, or other forms of foundation damage, understanding these methods can empower you to make the right choice for your property's stability and longevity.