Can a House with a Bad Foundation be Saved?
Basic Types of Foundations
Understanding the type of foundation your house has is crucial in determining the feasibility of repair. Houses can have various types of foundations, including slab-on-grade, crawl space, and basement foundations. Slab-on-grade foundations, commonly found in warmer climates, may be more susceptible to cracking due to soil movement, while houses with crawl space foundations may experience moisture issues leading to structural damage. Basements provide additional living or storage space below ground level and are constructed with concrete walls and footings, making them susceptible to bowing walls or water infiltration. Identifying the type of foundation your house has will help you better understand potential issues and repair options.
Slab-on-grade: These foundations are typically found in warmer climates and consist of a single concrete slab poured directly onto the ground.
Crawl space: Houses with crawl space foundations have a raised floor supported by piers or posts, allowing limited access beneath the house.
Basement foundations: Basements provide additional living or storage space below ground level and are constructed with concrete walls and footings.
Each type has its own characteristics and repair challenges. For example:
Slab-on-grade foundations may be more susceptible to cracking due to soil movement.
Crawl space foundations may be prone to moisture issues leading to structural damage.
Basement foundations may experience bowing walls or water infiltration.
Common Foundation Problems
Recognizing common foundation problems is essential for assessing the severity of the issue. Foundation problems can manifest in various ways, including cracks, settlement, and bowed walls. Cracks in the foundation or walls may indicate underlying structural issues, while settlement can cause uneven floors and sticking doors or windows. Bowed walls are another common problem, often caused by soil pressure or water damage. Understanding these common foundation problems will help homeowners identify when their house may be in need of repair.
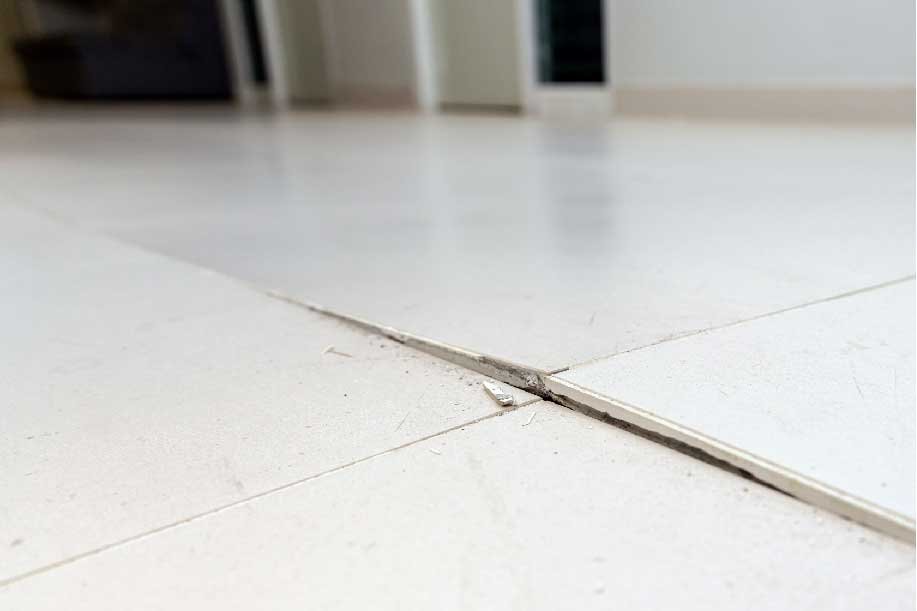
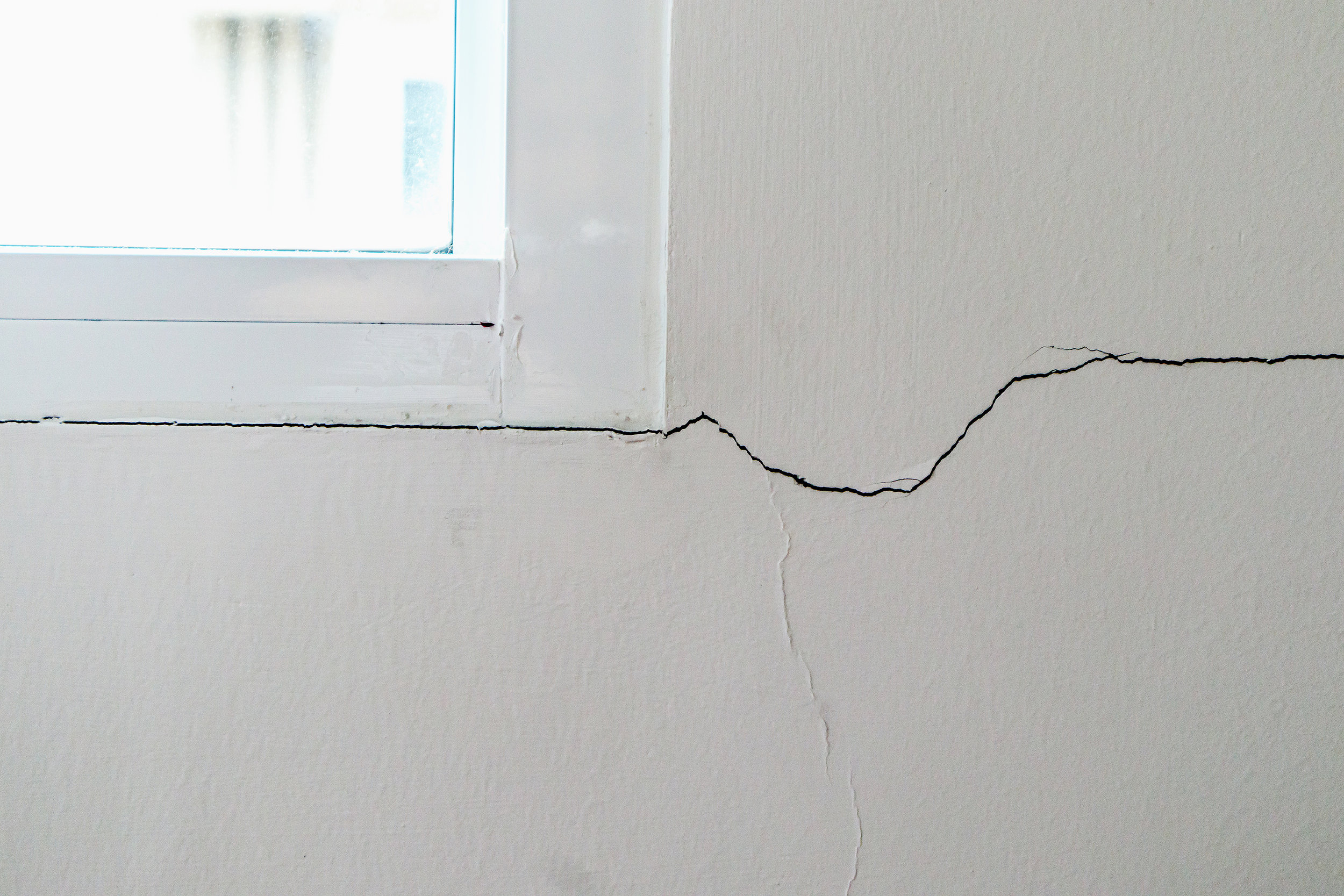
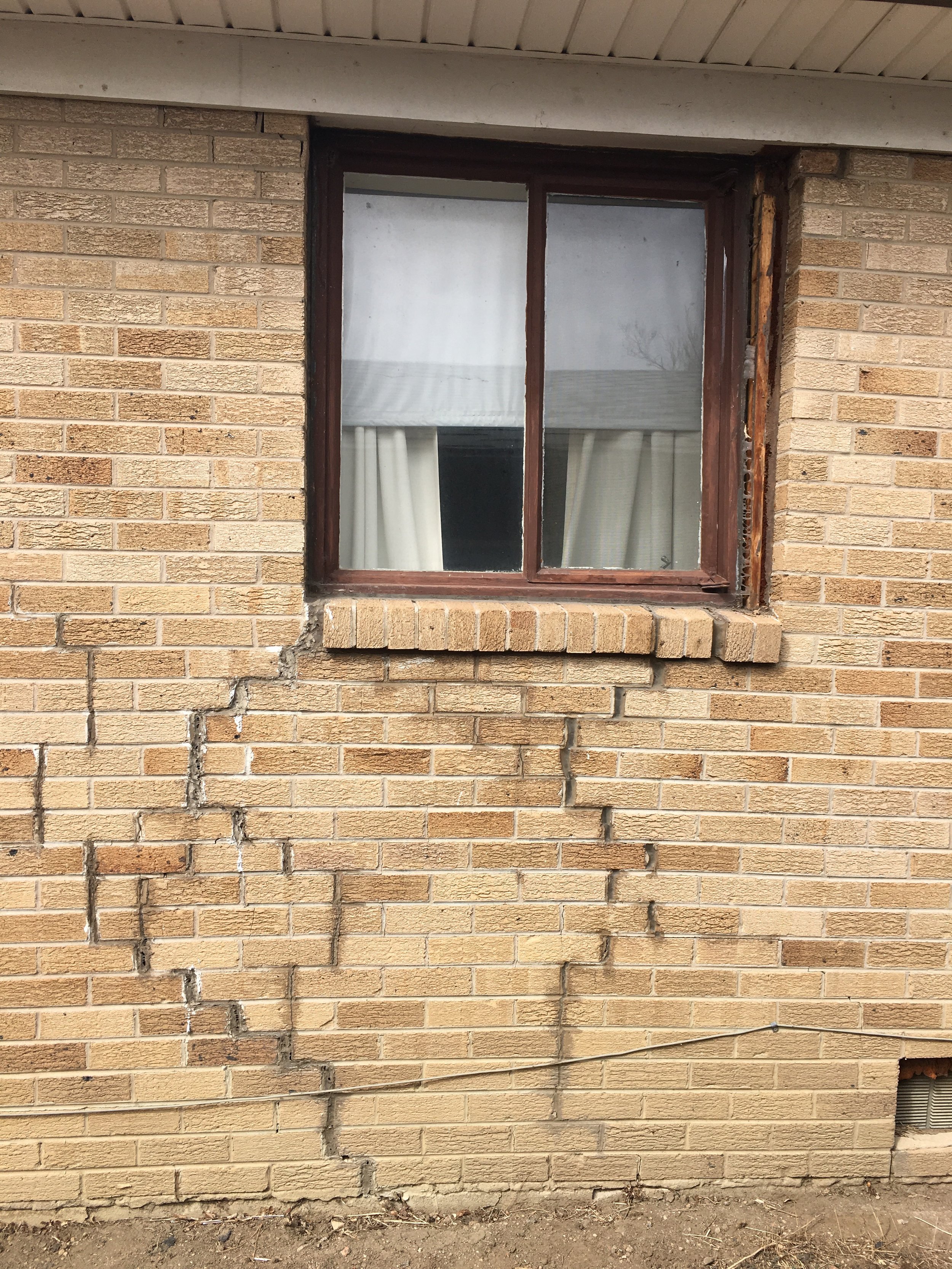
Cracks: Cracks in the foundation or walls are common signs of underlying issues. They vary in size and direction, indicating different levels of severity and potential structural movement.
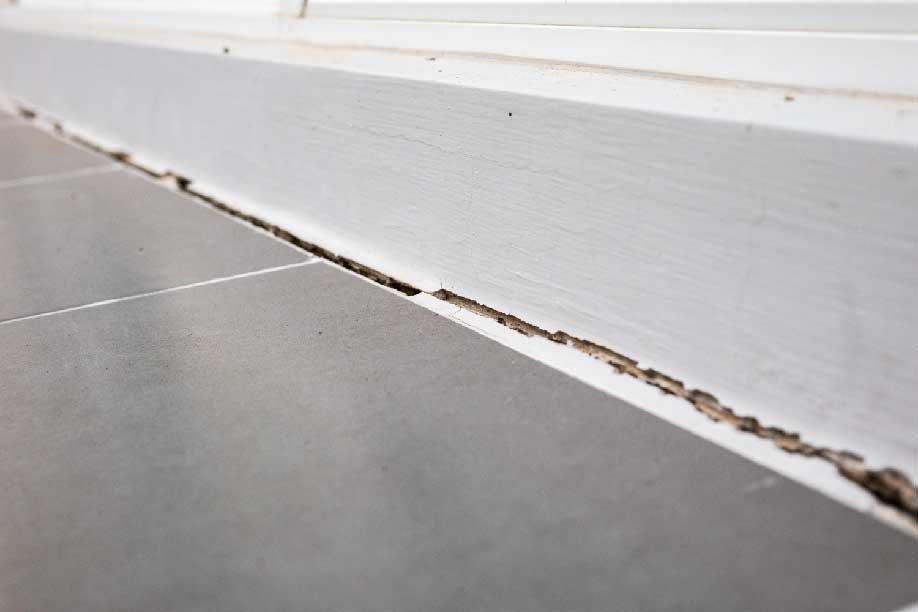
Settlement: Uneven floors, sloping areas, and gaps between walls and floors or ceilings signal foundation settlement. It's crucial to monitor these signs to assess the extent of the problem.
Bowed or Leaning Walls: Lateral pressure from soil or poor drainage can cause walls to bow or lean inward, compromising structural stability and integrity.
Water Damage: Excess moisture can lead to soil erosion, expansion, or hydrostatic pressure around the foundation, resulting in structural damage and mold growth.
Foundation Heaving: Upward movement of the foundation, often due to soil expansion, can cause cracks, uneven floors, and displacement of structural elements.
Sinking or Tilting Chimneys: Chimneys attached to the main structure may sink or tilt due to soil settlement or inadequate support, leading to structural issues and safety concerns.
These issues can indicate underlying structural issues that need prompt attention. Cracks, for instance, may vary in severity and could signify anything from minor settlement to significant structural instability.
Common Symptoms You Should Know:
Being able to recognize symptoms of foundation problems is crucial for prompt evaluation and repair. Common symptoms include uneven floors, sticking doors or windows, and visible cracks in walls or ceilings. Doors that no longer latch properly or windows that are difficult to open or close may indicate foundation settlement. Cracks in the walls or ceilings, especially those that are wider than a quarter-inch, may signal structural issues. Recognizing these symptoms early on can help prevent further damage to your home's foundation.
Uneven floors: Floors that slope or feel uneven may indicate foundation settlement or structural damage.
Doors or windows that stick: Changes in the shape or alignment of doorways and windows can signal foundation movement.
Cracks in walls: Visible cracks in interior or exterior walls, especially around doorways or windows, may be a sign of foundation issues.
Visible gaps between the walls and the ceiling or floor: Gaps or separations between building elements can indicate settlement or movement.
These symptoms can indicate foundation issues that require professional evaluation and repair.
What Can You Do If You Have Foundation Problems
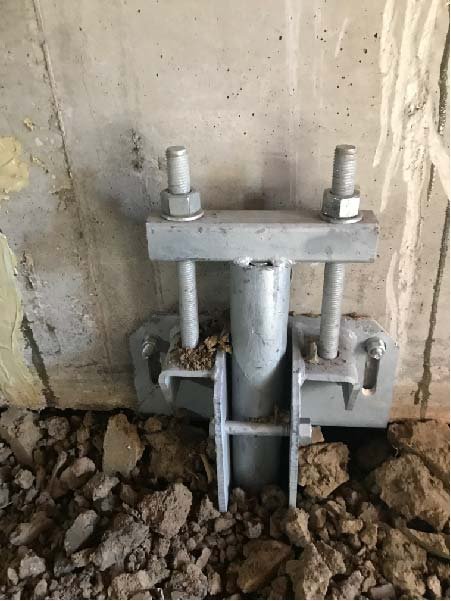
Upon discovering foundation issues, homeowners should consult with a professional foundation contractor to assess the extent of the damage and recommend appropriate repair solutions. Foundation repair methods vary depending on the type and severity of the problem. Options may include concrete piering, steel piers, helical piers, slab jacking, or epoxy injection. A qualified foundation contractor can provide expert advice on the best course of action for repairing your home's foundation.
Consult with a professional foundation contractor: A qualified contractor can assess the extent of the damage and recommend appropriate repair solutions.
Obtain multiple quotes: Get estimates from several reputable contractors to compare repair options and costs.
Consider the impact of repairs: Evaluate how repairs will affect the overall structure and value of the house.
Evaluate financing options: Explore financing options such as home equity loans or financing plans offered by contractors to fund the repairs.
Experiencing Foundation Issues?
Typical Costs of Foundation Repairs
Understanding the potential costs associated with foundation repairs is essential for budgeting and planning. Costs can vary depending on factors such as the type and extent of damage, the chosen repair method, and local labor and material prices. For example, concrete piering typically costs between $1,000 to $3,000 per pier, while epoxy injection can range from $200 to $2,000 or more for professional services. By understanding the typical costs of foundation repairs, homeowners can make informed decisions about their repair options.
The type and extent of damage
The chosen repair method
Local labor and material prices
Common repair methods and their typical costs include:
Concrete piering: $1,000 to $3,000 per pier
Steel piers: $1,000 to $3,000 per pier
Helical piers: $1,000 to $1,500 per pier
Slab jacking: $3 to $6 per square foot
Epoxy injection: $200 to $2,000 or more for professional services
When To Walk Away
In some cases, the severity of foundation problems or the cost of repairs may outweigh the benefits of salvaging the house. Knowing when it's time to walk away and consider alternative options can save you time, money, and stress in the long run. Factors to consider include the extent of the damage, the cost of repairs, and the overall condition of the house. If the foundation issues are too severe or the cost of repairs exceeds the value of the home, it may be more practical to explore other housing options.
The extent of damage and the potential for future issues
The cost of repairs compared to the value of the property
The feasibility of alternative options such as selling the property as-is
Knowing when it's time to walk away and consider alternative options can save you time, money, and stress in the long run.
Consider this article from Forbes for additional information on when to walk away from a bad foundation: https://www.forbes.com/home-improvement/foundation/when-to-walk-away-from-foundation-issues/ ➤